Generate Ssh Key Windows 7 Command Line
Sep 26, 2019 To generate an SSH key with PuTTYgen, follow these steps: Open the PuTTYgen program. For Type of key to generate, select SSH-2 RSA. Click the Generate button. Move your mouse in the area below the progress bar. When the progress bar is full, PuTTYgen generates your key pair. You can use the ssh-keygen command line utility to create RSA and DSA keys for public key authentication, to edit properties of existing keys, and to convert file formats. When no options are specified, ssh-keygen generates a 2048-bit RSA key pair and queries you for a key name and a passphrase to protect the private key.
- Generate Ssh Key Command Prompt
- Generate Ssh Key Windows 7 Command Line Commands
- Generate Ssh Key Windows 7 Command Line Commands
- Git Command Generate Ssh Key
- Generate Ssh Public Key Windows
Since there is no user associated with the sshd service, the host keys are stored under ProgramData ssh. User key generation. To use key-based authentication, you first need to generate some public/private key pairs for your client. From PowerShell or cmd, use ssh-keygen to generate some key files. Cd.ssh ssh-keygen. To create a new key pair, select the type of key to generate from the bottom of the screen (using SSH-2 RSA with 2048 bit key size is good for most people; another good well-known alternative is ECDSA). Then click Generate, and start moving the mouse within the Window. Putty uses mouse movements to. To generate the public/private key pair, enter this in the Command Prompt: ssh-keygen At the first prompt, “Enter file in which to save the key,” press Enter to save it in the default location.
- Gerrit Tutorial
- Setting up Git
- Set Up SSH Keys in Gerrit
- Prepare to work with Gerrit
- How to Submit a Patch
- How Code is reviewed in Gerrit
- Gerrit Useful Resources
- Selected Reading
SSH stands for Secure Shell or sometimes Secure Socket Shell protocol used for accessing network services securely from a remote computer. You can set the SSH keys to provide a reliable connection between the computer and Gerrit.
You can check the existing SSH key on your local computer using the following command in Git Bash −
After clicking the enter button, you will see the existing SSH key as shown in the following image −
If you don't find any existing SSH key, then you need to create a new SSH key.
Generating New SSH Key
You can generate a new SSH key for authentication using the following command in Git Bash −
If you already have a SSH key, then don't a generate new key, as they will be overwritten. You can use ssh-keygen command, only if you have installed Git with Git Bash.
When you run the above command, it will create 2 files in the ~/.ssh directory.
~/.ssh/id_rsa − It is private key or identification key.
~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub − It is a public tv.
Introduction
SSH (Secure Shell) is a network protocol that enables secure remote connections between two systems. System admins use SSH utilities to manage machines, copy, or move files between systems. Because SSH transmits data over encrypted channels, security is at a high level.
This article will guide you through the most popular SSH commands. The list can also serve as a cheat sheet and will come in handy the next time you need to complete a task.
- An SSH client of your choice
- An SSH server on the remote machine
- The IP address or name of the remote server
To connect to a remote machine, you need its IP address or name. Load the terminal or any SSH client and type ssh followed by the IP address:
or name:
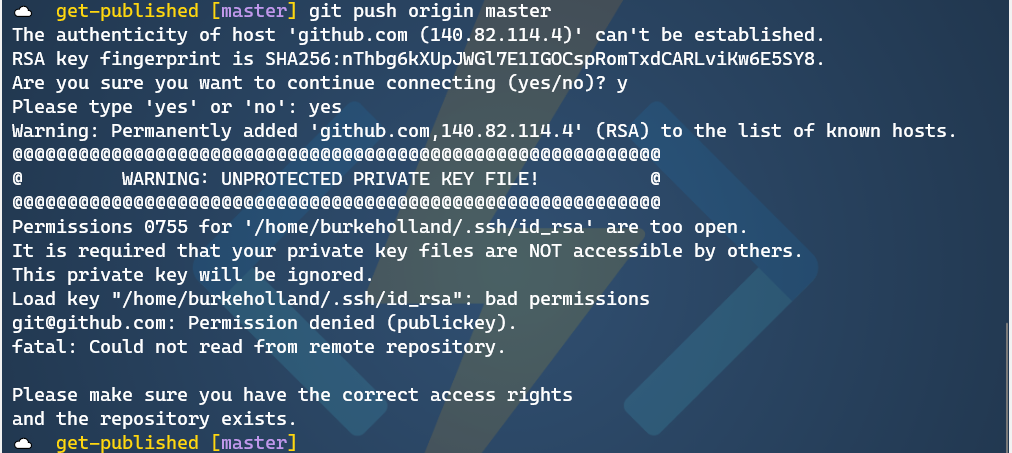
The first time you connect to a host, you’ll see this message:
Type yes and hit enter. You may need to enter your password as well.
SSH uses the current user when accessing a remote server. To specify a user for an SSH connection, run the command in this format:
For instance:
By default, the SSH server listens for a connection on port 22. If the port setting in the SSH config file has been changed, you’ll need to specify the port. Otherwise, you will get this error:
To connect to a remote host with a custom SSH port number, use the -pflag. For example:
To improve the security of SSH connections, generate a key pair with the keygen utility. The pair consists of a public and private key. The public key can be shared, while the private key needs to stay secure.
SSH key pairs are used to authenticate clients to servers automatically. When you create an SSH key pair, there is no longer a need to enter a password to access a server.
On the host machine’s terminal, use this command to create a key pair:
To use default settings, hit Enter on the prompts for file location and passphrase.
To use the key pair for SSH authentication, you’ll need to copy the public key to a server. The key is the file id_rsa.pub previously created with SSH keygen utility.
To copy your key to a server, run this command from the client:
You can also specify a username if you don’t want to use the current user.
Enter the password to authenticate when asked. After this, you will no longer need to use the password to connect to the same server.
You can securely copy files over the SSH protocol using the SCP tool. The basic syntax is:
For example, to copy a file sample3 to your Desktop on a remote server with a username test, type in:
Nfs shift 2 serial key generator. The output shows a summary of the operation.
Make sure to use the uppercase-Pflag if you need to specify the port.
You can control how remote users can access a server via the SSH. Edit the settings in the sshd_config file to customize SSH server options. Make sure to edit only the options you are familiar with. A server can become inaccessible due to bad configuration.
Use the editor of your choice to edit the file. You’ll need superuser permissions to make changes. In Linux, we use vim:
In the command line on a remote host, type in:
Enter the sudo password, and the shell opens the file in the editor you used.
When you make changes to the SSH configuration, you’ll need to restart the service in Linux.
Depending on the Linux distro, run one of the following commands on the machine where you modified the settings:
or:
Finally, enter the password to complete the process. As a result, the next SSH session will use the new settings.
Working on a remote server using SSH requires knowing basic SSH commands. Use the commands and options in this article to manage a remote host. Note that you can combine the flags to get the output you need.
Use the pwd command to show the file system path.
The output displays the location of the directory you are in.
To list the contents of a current working folder, use the ls command.
The shell will show the names of all directories, files, and links. To get more information, add one of the following flags:
-adisplays hidden files and entries starting with a dot.-lshows file details for directory contents. For example, the output includes permissions, ownership, date, etc.-slists the size of files, in blocks. Add -h to show the size in a humanly-readable form.
To navigate to a specific folder, use the cd command and a name or path of a directory.
Remember that the names are case sensitive. Use cd without a name or path to return to the user’s home directory.
Useful cd options include:
cd .go to the directory one level higher than your current location.cd -switch to the previous directory.cd /go to the root directory.
Use the cp command to copy a file or directory. You’ll need to include the name of the file and the target location.
To copy file1 from Desktop to Dir1, type in:
To change the name of file1 while copying it to another destination, use this format:
This command copies file1 to Dir1 with a name you specify.
Generate Ssh Key Command Prompt
To copy a directory and its contents, use the -r flag in this format:
The mv command works in the same manner as the copy command.
For instance, to move a file to another location, type in:
The touch command allows you to create a new file with any extension.
In the terminal, enter the following command:
For example, to create a system.log file, type in:
To create a directory, use the mkdir command. Enter a new directory name or full path in this format:
Or:
To delete a Linux file , use rm in this format:
In addition, you can enter a full path:
To delete a directory, add the -r flag to the rm command.
To view the status of all network adapters, use the ifconfig command. Moreover, when you don’t use any options with ifconfig, the output displays only active interfaces.
To clear the current working area of your bash screen, type clear in the shell. This command clears one portion of the screen and shifts up the previous output.
To remove the output from the terminal completely, use the reset command.
Run a Command on a Remote Server from a Local Computer
Generate Ssh Key Windows 7 Command Line Commands
This method does not create a new shell. Instead, it runs a command and returns the user to the local prompt. You can create a file, copy files, or run any other SSH command in this format.
To remotely execute a command from the local machine, append an instruction to the SSH command. For example, to delete a file, type in:
Enter the password, and the file on the remote server will be deleted without creating a new shell.
Generate Ssh Key Windows 7 Command Line Commands
The SSH tool comes with many optional parameters. The table below lists common SSH options and the corresponding descriptions.
| SSH Option | Description |
| -1 | Instructs ssh to use protocol version 1 |
| -2 | Instructs ssh to use protocol version 2. |
| -4 | Permits only IPv4 addresses. |
| -6 | Permits only IPv6 addresses. |
| -A | Enables authentication agent connection forwarding. Use this option with caution. |
| -a | Disables authentication agent connection forwarding. |
| -b bind_address | Use this option on the local host with more than one address to set the source address of the connection. |
| -C | Enables data compression for all files. Only to be used with slow connections. |
| -c cipher_spec | Use to select a cipher specification. List the values separated by a comma. |
| -E log_fileName | Attaches debug logs to log_file instead of standard error. |
| -f | Sends ssh to background, even before entering a password or passphrase. |
| -g | Permits remote hosts to connect to ports forwarded on a local machine. |
| -q | Runs ssh in quiet mode. It suppresses most error or warning messages. |
| -V | Displays the version of ssh tool and exits. |
| -v | Prints debugging messages for ssh connection. The verbose mode is useful when troubleshooting configuration issues. |
| -X | Use this option to enable X11 forwarding. |
| -x | Disable X11 forwarding. |
This article has covered the 19 most popular commands for using the SSH tool effectively. Now you can manage your server remotely with an added layer of security and have these commands at your fingertips.
Git Command Generate Ssh Key
Before executing these commands and options on a live server, we do recommend using a test machine first.
Next you should also read
The article covers the 5 most common and efficient ways to secure an SSH connection. The listed solutions go…
This article provides all the information you need in order to set up SSH encryption on your remote device.…
If you are using Debian 9 or Debian 10 to manage servers, you must ensure that the transfer of data is as…
Generate Ssh Public Key Windows
When establishing a remote connection between a client and a server, a primary concern is ensuring a secure…
MySQL is an open-source relational database server tool for Linux operating systems. It is widely used in…